Java LinkedList is a doubly linked list implementation of Java’s List and Deque interfaces. It is part of Java’s collections framework. Here is the class hierarchy of LinkedList
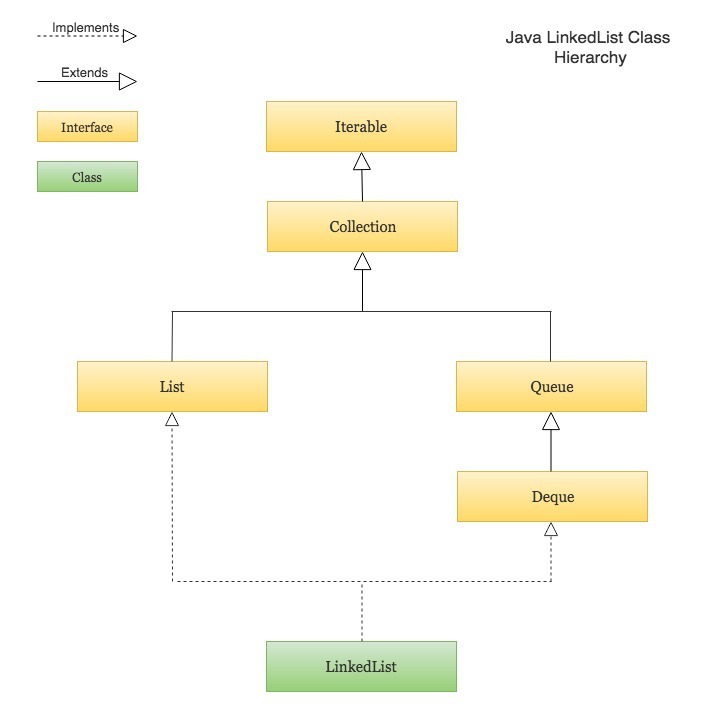
Following are some key points to note about LinkedList in Java –
- Java LinkedList maintains the insertion order of the elements.
- LinkedList can have duplicate and null values.
- The LinkedList class implements
QueueandDequeinterfaces. Therefore, It can also be used as aQueue,DequeorStack. - Java LinkedList is not thread-safe. You must explicitly synchronize concurrent modifications to the LinkedList in a multi-threaded environment.
Java ArrayList vs LinkedList
Both ArrayList and LinkedList implement the List interface. However, they differ completely in the way they store and link to the elements.
An ArrayList stores the elements sequentially based on their index. However, a LinkedList uses a doubly-linked list to store its elements.
A doubly-linked list consists of a collection of nodes, where each node contains three fields –
- The data at that node.
- A pointer/reference to the next node in the list.
- A pointer/reference to the previous node in the list.
Following is a visual of ArrayList and LinkedList data structures:

Following are some key differences between LinkedList and ArrayList:
- A LinkedList consumes more memory than an ArrayList because it also stores the next and previous references along with the data.
- You can access an element in an ArrayList in
O(1)time. But it takesO(n)time to access an element in a LinkedList because it needs to traverse to the desired element by following the next/prev references. - Adding or removing elements are usually slower in an ArrayList compared to LinkedList. This is because the elements in the ArrayList needs to be shifted if a new element is added in the middle of the ArrayList. The ArrayList might also need to be resized to accommodate the new element. Similarly, in case of removal, the elements in the ArrayList needs to be shifted to the new positions.
Creating a LinkedList and adding new elements to it
The following example shows how to create a LinkedList and add new elements to it. Notice the uses of addFirst() and addLast() methods in the example. These methods come from the Deque interface.
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class CreateLinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a LinkedList
LinkedList<String> friends = new LinkedList<>();
// Adding new elements to the end of the LinkedList using add() method.
friends.add("Rajeev");
friends.add("John");
friends.add("David");
friends.add("Chris");
System.out.println("Initial LinkedList : " + friends);
// Adding an element at the specified position in the LinkedList
friends.add(3, "Lisa");
System.out.println("After add(3, \"Lisa\") : " + friends);
// Adding an element at the beginning of the LinkedList
friends.addFirst("Steve");
System.out.println("After addFirst(\"Steve\") : " + friends);
// Adding an element at the end of the LinkedList (This method is equivalent to the add() method)
friends.addLast("Jennifer");
System.out.println("After addLast(\"Jennifer\") : " + friends);
// Adding all the elements from an existing collection to the end of the LinkedList
List<String> familyFriends = new ArrayList<>();
familyFriends.add("Jesse");
familyFriends.add("Walt");
friends.addAll(familyFriends);
System.out.println("After addAll(familyFriends) : " + friends);
}
}
# Output
Initial LinkedList : [Rajeev, John, David, Chris]
After add(3, "Lisa") : [Rajeev, John, David, Lisa, Chris]
After addFirst("Steve") : [Steve, Rajeev, John, David, Lisa, Chris]
After addLast("Jennifer") : [Steve, Rajeev, John, David, Lisa, Chris, Jennifer]
After addAll(familyFriends) : [Steve, Rajeev, John, David, Lisa, Chris, Jennifer, Jesse, Walt]
Retrieving elements from a LinkedList
The following example shows:
- How to get the first element in the LinkedList.
- How to get the last element in the LinkedList.
- How to get the element at a given index in the LinkedList.
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class RetrieveLinkedListElementsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// A LinkedList containing Stock Prices of a company for the last 6 days
LinkedList<Double> stockPrices = new LinkedList<>();
stockPrices.add(45.00);
stockPrices.add(51.00);
stockPrices.add(62.50);
stockPrices.add(42.75);
stockPrices.add(36.80);
stockPrices.add(68.40);
// Getting the first element in the LinkedList using getFirst()
// The getFirst() method throws NoSuchElementException if the LinkedList is empty
Double firstElement = stockPrices.getFirst();
System.out.println("Initial Stock Price : " + firstElement);
// Getting the last element in the LinkedList using getLast()
// The getLast() method throws NoSuchElementException if the LinkedList is empty
Double lastElement = stockPrices.getLast();
System.out.println("Current Stock Price : " + lastElement);
// Getting the element at a given position in the LinkedList
Double stockPriceOn3rdDay = stockPrices.get(2);
System.out.println("Stock Price on 3rd Day : " + stockPriceOn3rdDay);
}
}
# Output
Initial Stock Price : 45.0
Current Stock Price : 68.4
Stock Price on 3rd Day : 62.5
Removing elements from a LinkedList
The example below shows:
- How to remove the first element in the LinkedList.
- How to remove the last element in the LinkedList.
- How to remove the first occurrence of a given element in the LinkedList.
- How to remove all the elements that satisfy a given predicate from the LinkedList.
- How to clear the LinkedList completely.
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class RemoveElementsFromLinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> programmingLanguages = new LinkedList<>();
programmingLanguages.add("Assembly");
programmingLanguages.add("Fortran");
programmingLanguages.add("Pascal");
programmingLanguages.add("C");
programmingLanguages.add("C++");
programmingLanguages.add("Java");
programmingLanguages.add("C#");
programmingLanguages.add("Kotlin");
System.out.println("Initial LinkedList = " + programmingLanguages);
// Remove the first element in the LinkedList
String element = programmingLanguages.removeFirst(); // Throws NoSuchElementException if the LinkedList is empty
System.out.println("Removed the first element " + element + " => " + programmingLanguages);
// Remove the last element in the LinkedList
element = programmingLanguages.removeLast(); // Throws NoSuchElementException if the LinkedList is empty
System.out.println("Removed the last element " + element + " => " + programmingLanguages);
// Remove the first occurrence of the specified element from the LinkedList
boolean isRemoved = programmingLanguages.remove("C#");
if(isRemoved) {
System.out.println("Removed C# => " + programmingLanguages);
}
// Remove all the elements that satisfy the given predicate
programmingLanguages.removeIf(programmingLanguage -> programmingLanguage.startsWith("C"));
System.out.println("Removed elements starting with C => " + programmingLanguages);
// Clear the LinkedList by removing all elements
programmingLanguages.clear();
System.out.println("Cleared the LinkedList => " + programmingLanguages);
}
}
# Output
Initial LinkedList = [Assembly, Fortran, Pascal, C, C++, Java, C#, Kotlin]
Removed the first element Assembly => [Fortran, Pascal, C, C++, Java, C#, Kotlin]
Removed the last element Kotlin => [Fortran, Pascal, C, C++, Java, C#]
Removed C# => [Fortran, Pascal, C, C++, Java]
Removed elements starting with C => [Fortran, Pascal, Java]
Cleared the LinkedList => []
Searching for elements in a LinkedList
The example below shows:
- How to check if an element exists in a LinkedList.
- How to find the index of the first occurrence of an element in the LinkedList.
- How to find the index of the last occurrence of an element in the LinkedList.
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class SearchLinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> employees = new LinkedList<>();
employees.add("John");
employees.add("David");
employees.add("Lara");
employees.add("Chris");
employees.add("Steve");
employees.add("David");
// Check if the LinkedList contains an element
System.out.println("Does Employees LinkedList contain \"Lara\"? : " + employees.contains("Lara"));
// Find the index of the first occurrence of an element in the LinkedList
System.out.println("indexOf \"Steve\" : " + employees.indexOf("Steve"));
System.out.println("indexOf \"Mark\" : " + employees.indexOf("Mark"));
// Find the index of the last occurrence of an element in the LinkedList
System.out.println("lastIndexOf \"David\" : " + employees.lastIndexOf("David"));
System.out.println("lastIndexOf \"Bob\" : " + employees.lastIndexOf("Bob"));
}
}
# Output
Does Employees LinkedList contain "Lara"? : true
indexOf "Steve" : 4
indexOf "Mark" : -1
lastIndexOf "David" : 5
lastIndexOf "Bob" : -1
Iterating over a LinkedList
The following example shows how to iterate over a LinkedList using
- Java 8
forEach()and lambda expression. - iterator()
- iterator() and Java 8 forEachRemaining() method
- descendingIterator()
- listIterator()
- simple for-each loop.
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class IterateOverLinkedListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<String> humanSpecies = new LinkedList<>();
humanSpecies.add("Homo Sapiens");
humanSpecies.add("Homo Neanderthalensis");
humanSpecies.add("Homo Erectus");
humanSpecies.add("Home Habilis");
System.out.println("=== Iterate over a LinkedList using Java 8 forEach and lambda ===");
humanSpecies.forEach(name -> {
System.out.println(name);
});
System.out.println("\n=== Iterate over a LinkedList using iterator() ===");
Iterator<String> humanSpeciesIterator = humanSpecies.iterator();
while (humanSpeciesIterator.hasNext()) {
String speciesName = humanSpeciesIterator.next();
System.out.println(speciesName);
}
System.out.println("\n=== Iterate over a LinkedList using iterator() and Java 8 forEachRemaining() method ===");
humanSpeciesIterator = humanSpecies.iterator();
humanSpeciesIterator.forEachRemaining(speciesName -> {
System.out.println(speciesName);
});
System.out.println("\n=== Iterate over a LinkedList using descendingIterator() ===");
Iterator<String> descendingHumanSpeciesIterator = humanSpecies.descendingIterator();
while (descendingHumanSpeciesIterator.hasNext()) {
String speciesName = descendingHumanSpeciesIterator.next();
System.out.println(speciesName);
}
System.out.println("\n=== Iterate over a LinkedList using listIterator() ===");
// ListIterator can be used to iterate over the LinkedList in both forward and backward directions
// In this example, we start from the end of the list and traverse backwards
ListIterator<String> humanSpeciesListIterator = humanSpecies.listIterator(humanSpecies.size());
while (humanSpeciesListIterator.hasPrevious()) {
String speciesName = humanSpeciesListIterator.previous();
System.out.println(speciesName);
}
System.out.println("\n=== Iterate over a LinkedList using simple for-each loop ===");
for(String speciesName: humanSpecies) {
System.out.println(speciesName);
}
}
}
# Output
=== Iterate over a LinkedList using Java 8 forEach and lambda ===
Homo Sapiens
Homo Neanderthalensis
Homo Erectus
Home Habilis
=== Iterate over a LinkedList using iterator() ===
Homo Sapiens
Homo Neanderthalensis
Homo Erectus
Home Habilis
=== Iterate over a LinkedList using iterator() and Java 8 forEachRemaining() method ===
Homo Sapiens
Homo Neanderthalensis
Homo Erectus
Home Habilis
=== Iterate over a LinkedList using descendingIterator() ===
Home Habilis
Homo Erectus
Homo Neanderthalensis
Homo Sapiens
=== Iterate over a LinkedList using listIterator() ===
Home Habilis
Homo Erectus
Homo Neanderthalensis
Homo Sapiens
=== Iterate over a LinkedList using simple for-each loop ===
Homo Sapiens
Homo Neanderthalensis
Homo Erectus
Home Habilis
Conclusion
That’s all folks! In this article, you learned what is a LinkedList, what are the differences between a LinkedList and an ArrayList, how to create a LinkedList, how to add, remove and search for elements in a LinkedList, and how to iterate over a LinkedList.
Thanks for reading. Have a good day! This article is from callicoder


